Dry Type vs Oil Transformers: Which One Is Right for Your Facility?
Choosing the right transformer for your facility is a critical decision that impacts safety, efficiency, maintenance costs, and overall operational reliability. Transformers are the backbone of electrical distribution systems, whether in commercial buildings, industrial plants, or utility networks. Among the most common options are dry-type transformers and oil-filled transformers. Each has its unique advantages and limitations, but for many modern facilities, dry-type transformers are increasingly preferred due to their safety, low maintenance and environmental benefits.
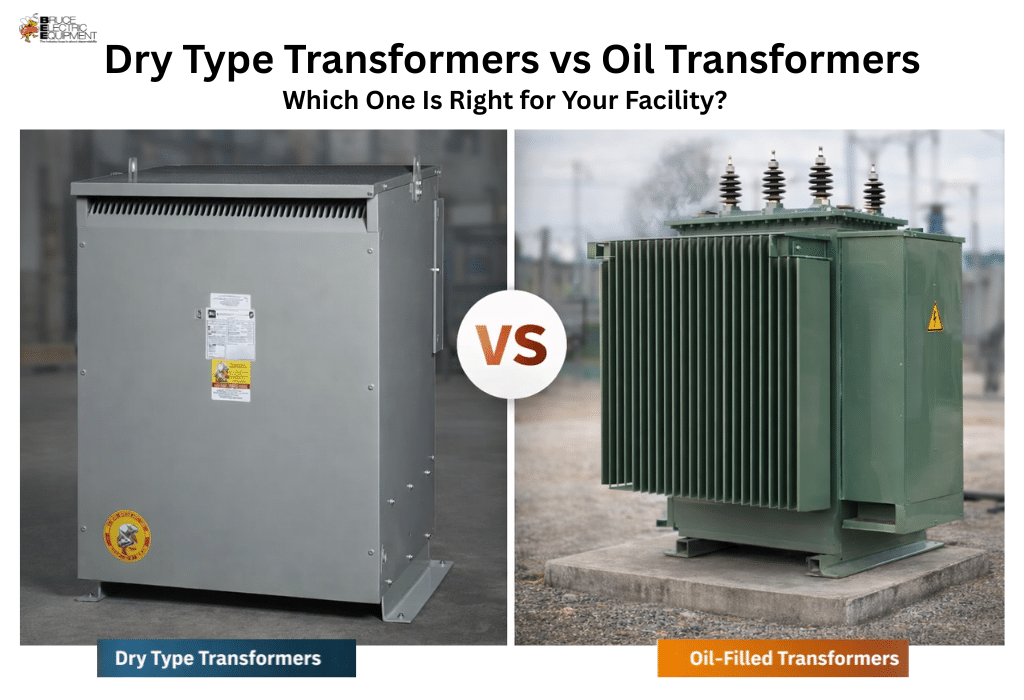
What Are Dry-Type Transformers?
Dry-type transformers are electrical devices that transfer electrical energy without the use of liquid insulation. Instead of oil, they rely on air and specially designed insulating materials to cool and protect the windings. These transformers are widely used in commercial buildings, industrial facilities, hospitals, data centers, and schools, where safety and low maintenance are essential.
Key Features of Dry-Type Transformers:
• Air-cooled insulation: No oil means lower fire risk and safer indoor installation.
• Compact design: Dry-type transformers are often smaller and lighter than oil-filled models, making them easier to install in tight spaces.
• Environmentally friendly: Without oil, there’s no risk of leaks or soil contamination.
• Low maintenance: No need for regular oil testing or replacement, which reduces long-term operational costs.
Typical Applications:
• Hospitals and healthcare facilities
• Data centers and IT infrastructure
• Commercial buildings and high-rise offices
• Industrial plants requiring indoor installation
What are Oil-Filled Transformers?
Oil-filled transformers, as the name suggests, use mineral oil or other insulating fluids to cool and insulate the windings. They have been widely used in outdoor and high-capacity applications, including utility substations and large industrial installations.
Key Features of Oil-Filled Transformers:
• Liquid insulation: Oil provides excellent heat dissipation, enabling higher capacity and longer runs between maintenance.
• High efficiency in large systems: Particularly suitable for large voltage ratings and heavy-duty industrial loads.
• Outdoor suitability: Typically installed outdoors due to the risk of fire hazards and oil leaks indoors.
Typical Applications:
• Utility substations and power generation facilities
• Large industrial plants with high voltage requirements
• Outdoor distribution systems
Limitations of Oil-Filled Transformers:
• Fire risk: Oil is highly flammable, which increases safety concerns indoors.
• Environmental hazards: Oil leaks can contaminate soil and require costly remediation.
• Higher maintenance: Requires regular oil testing, filtration, and occasional replacement.
While oil-filled transformers remain essential for certain high-capacity or outdoor installations, modern indoor facilities are increasingly choosing dry-type transformers for safety and maintenance benefits.
Why dry-type transformers are preferred: The combination of safety, durability, and minimal maintenance makes dry-type transformers an ideal choice for facilities that prioritize both operational reliability and environmental compliance.
Dry Type vs Oil-Filled: Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | Dry-Type Transformers | Oil-Filled Transformers |
| Cooling & Insulation | Air and resin-impregnated insulation | Mineral oil or insulating fluid |
| Fire Risk | Very low (ideal for indoor use) | Higher, requires fire precautions |
| Maintenance | Minimal, periodic inspection only | Moderate to high (oil testing, filtration) |
| Environmental Impact | No oil; eco-friendly | Potential soil contamination from leaks |
| Installation Location | Indoor or semi-indoor | Mostly outdoor; requires safety clearance |
| Noise Level | Low | Moderate to high, especially under load |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost, low lifetime cost | Often lower initial cost for large units, higher lifetime cost due to maintenance |
How to Choose the Right Transformer for Your Facility
Selecting the right transformer involves considering multiple factors:
1. Facility Type and Location
• Indoor facilities, such as hospitals or office buildings, often require dry-type transformers due to fire safety regulations and ease of installation.
• Outdoor substations or heavy industrial plants may still favor oil-filled transformers for high-capacity needs.
2. Load Requirements
Evaluate the voltage, current, and expected load to determine transformer size and type. Dry-type transformers handle medium-voltage distribution well, but for extremely high voltages, oil-filled transformers may still be necessary.
3. Maintenance Capabilities
• If your facility wants to minimize ongoing maintenance and reduce the need for specialized personnel, dry-type transformers are advantageous.
• Oil-filled transformers require routine oil testing and monitoring, which adds labor and operational costs.
4. Safety & Environmental Considerations
• Indoor installations and facilities with stringent fire safety regulations are ideal for dry-type transformers.
• For environmentally sensitive areas, avoiding oil leaks can prevent contamination and comply with regulations.
5. Budget & Lifecycle Cost
• Dry-type transformers may have a slightly higher upfront cost for certain capacities, but lower maintenance costs and longer operational safety often make them more cost-effective over the lifetime.
• Oil-filled transformers might be cheaper initially, but additional maintenance, fire mitigation, and environmental compliance costs increase long-term expenses.
Transformer Maintenance Tips: Dry-Type and Oil-Filled
Dry-Type Transformer Maintenance Tips
Dry-type transformers require relatively low maintenance, but regular checks are essential for safe and reliable operation.
• Dry-type transformers require relatively low maintenance, but regular checks are essential for safe and reliable operation.
• Keep the transformer clean: Remove dust and debris from coils, vents, and enclosures to maintain proper airflow.
• Ensure proper ventilation: Maintain adequate clearance around the unit to prevent overheating.
• Monitor temperature and load: Avoid overloading and watch for abnormal temperature rise.
• Inspect electrical connections: Tighten loose terminals and check grounding connections periodically.
• Listen for unusual noise: Excessive humming or vibration may indicate loose components or internal issues.
• Check insulation condition: Look for signs of discoloration, cracking, or moisture intrusion.
Oil-Filled Transformer Maintenance Tips
Oil-filled transformers require more frequent and specialized maintenance due to liquid insulation.
• Perform regular oil testing: Check oil quality for moisture, acidity, and dissolved gases.
• Inspect for oil leaks: Look for signs of leakage around gaskets, valves, and radiators.
• Monitor oil level and temperature: Ensure oil levels are within recommended limits and operating temperatures remain stable.
• Check cooling components: Inspect radiators, fans, and pumps for proper operation.
• Examine bushings and seals: Look for cracks, contamination, or wear that could lead to failures.
• Maintain proper spill containment: Ensure bunds and containment systems are intact and compliant with safety regulations.
Transformer Repair Considerations
Transformer repair plays a critical role in extending equipment lifespan and preventing unplanned downtime. Dry-type transformers generally require less frequent repair due to the absence of oil-related failures, but issues such as insulation degradation, loose connections, overheating, or abnormal noise may still require professional transformer repair services. Oil-filled transformers, on the other hand, often demand more complex repair work, including oil purification, leak sealing, gasket replacement, and bushing repairs. Timely transformer repair not only restores performance but also helps facilities avoid costly replacements, safety risks, and regulatory non-compliance. Regular inspections combined with proactive transformer repair strategies ensure reliable power distribution and long-term operational efficiency.
FAQs
Q1: Which is better, an oil type or dry type transformer?
A) Dry type transformers are ideal for indoor, commercial, and industrial use due to safety and low maintenance, while oil-filled transformers offer higher cooling efficiency and are better for outdoor or heavy-load applications. Choosing depends on your installation environment and power needs.
Q2: Why are transformers filled with oil?
A) Transformer oil acts as an insulator and coolant, preventing overheating and electrical breakdown, which ensures safe and efficient operation of oil-filled transformers in high-voltage applications.
Q3: What is another name for a dry type transformer?
A) A dry type transformer is also known as an air-cooled transformer or cast resin transformer, commonly used for safe, indoor, and environmentally friendly power distribution
Q4: What is the process of transformer repair?
A) Transformer repair involves inspection and testing to identify faults, followed by corrective actions such as tightening connections, repairing insulation, replacing damaged components, and performing electrical tests to restore safe and reliable operation.
Q5: What is OC and SC test on transformer?
A) The Open Circuit (OC) test measures core losses and magnetizing current, while the Short Circuit (SC) test determines copper losses and impedance, helping evaluate transformer efficiency and performance under load.
Conclusion
Choosing between dry-type and oil-filled transformers ultimately depends on your facility’s installation environment, load demands, safety requirements, and long-term maintenance strategy. While oil-filled transformers continue to serve high-capacity and outdoor applications effectively, dry-type transformers are increasingly preferred for indoor and commercial facilities due to their lower fire risk, reduced maintenance needs, and environmental advantages. Understanding ongoing maintenance requirements and knowing when transformer repair is necessary can significantly extend equipment lifespan and prevent costly downtime. By evaluating both operational needs and total lifecycle costs, facilities can select a transformer solution that delivers reliable performance, regulatory compliance, and long-term efficiency.